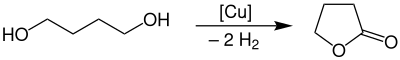Gamma-Butyrolactone
Gamma-Butyrolactone
Gamma-butyrolactone or γ-butyrolactone is a hygroscopic, colorless, water-miscible liquid with a weak, characteristic odor. It is the simplest 4-carbon lactone. It is mainly used as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, such as N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone.
In humans, GBL acts as a prodrug for gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) and is often used as a recreational drug. GHB acts as a central nervous system (CNS) depressant with effects similar to those of barbiturates.
GBL Occurrence
GBL has been found in extracts from samples of unadulterated wines. This finding indicates that GBL is a naturally occurring component in some wines and may be present in similar products. The concentration detected was approximately 5 μg/mL and was easily observed using a simple extraction technique followed by GC/MS analysis. GBL can be found in cheese flavorings but typically results in a content of 0.0002% GBL in the final foodstuff.
Production And Synthesis
γ-Butyrolactone is produced industrially by dehydrogenation of 1,4-butanediol at a temperature of 180–300 °C and atmospheric pressure in the presence of a copper catalyst.
The yield of this process is approximately 95%. The purification takes place with a liquid-gas-phase extraction.
In the laboratory, it may also be obtained via the oxidation of tetrahydrofuran (THF), for example with aqueous sodium bromate. An alternative route proceeds from GABA via a diazonium intermediate.
Showing the single result